- Published on
Internationalize .NET API Application
- Authors
- Name
- Yujia Sun
Though it is hard to use and the documentation is difficult to understand for a newbie, .NET, actually, provides some tools to internationalize your .NET API application without any third-party dependency. This blog summarizes necessary procedures to do it.
Code for this guide can be found here: wave-ys/dotnet-web-api-i18n-demo
Add localization files
Resources and add a resource file Localization.FooLocalization.resx under it: 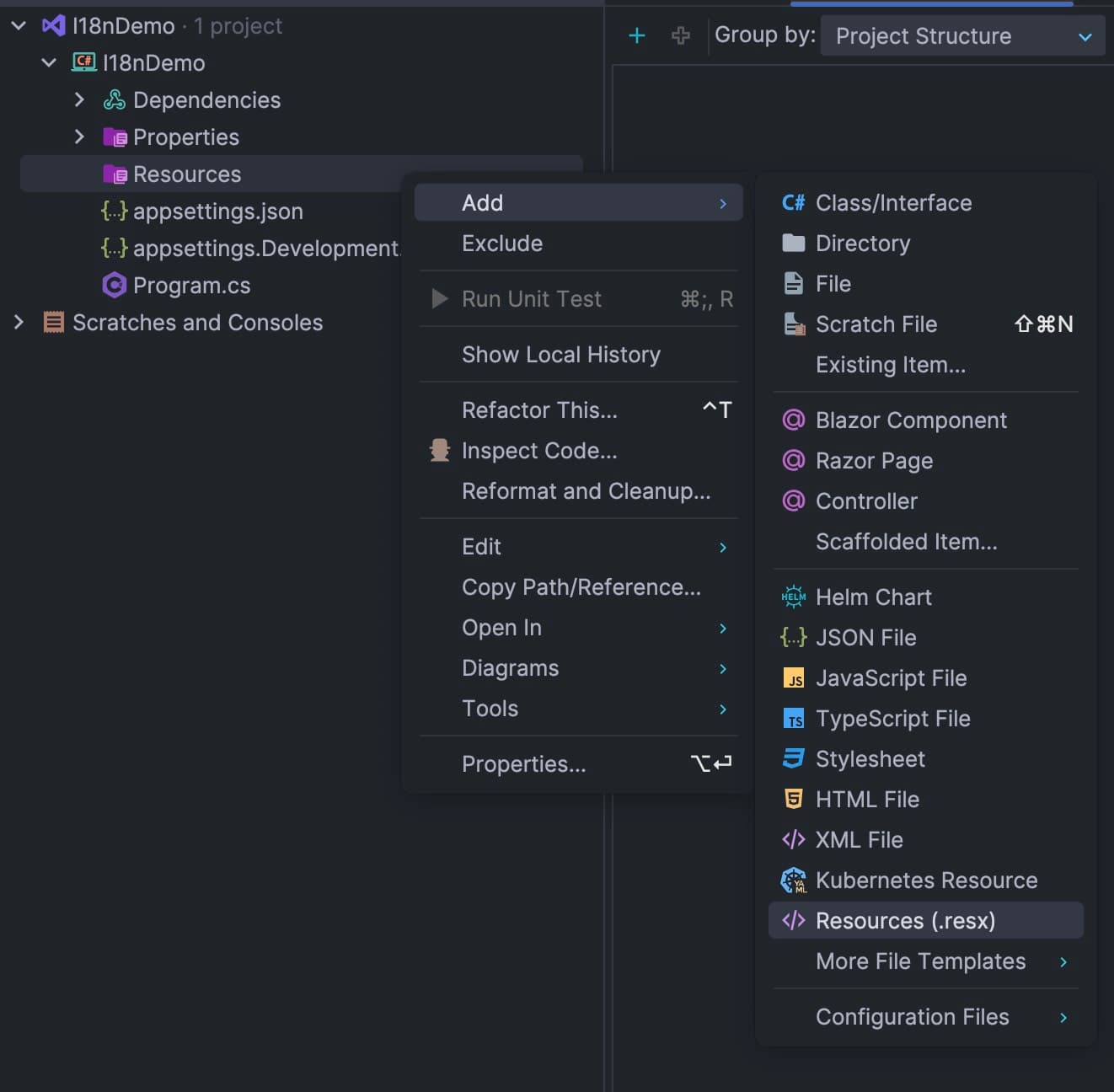
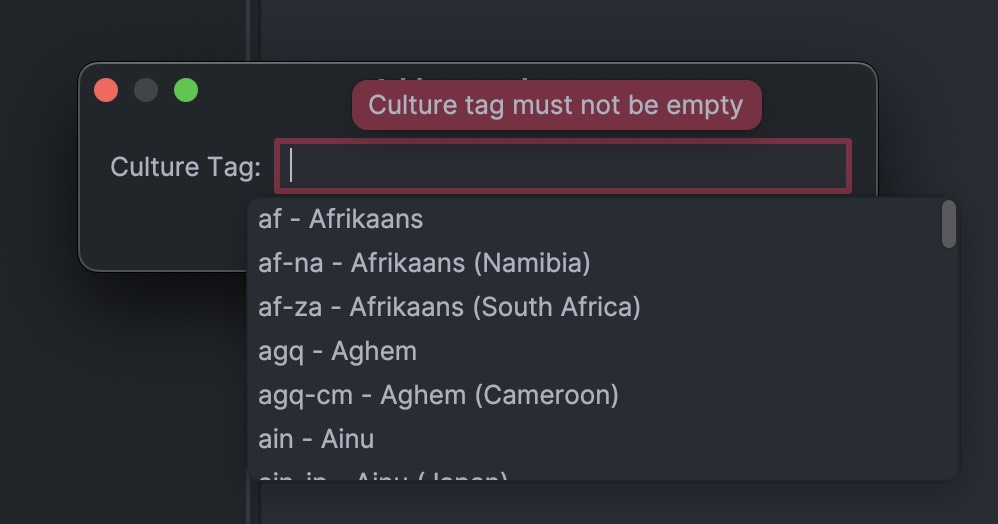
en-us and zh-hans-cn: 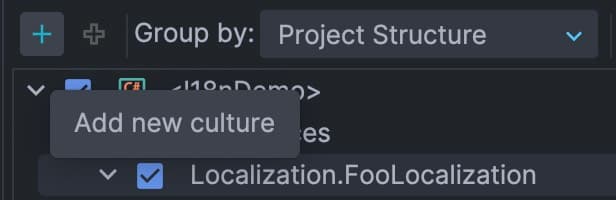
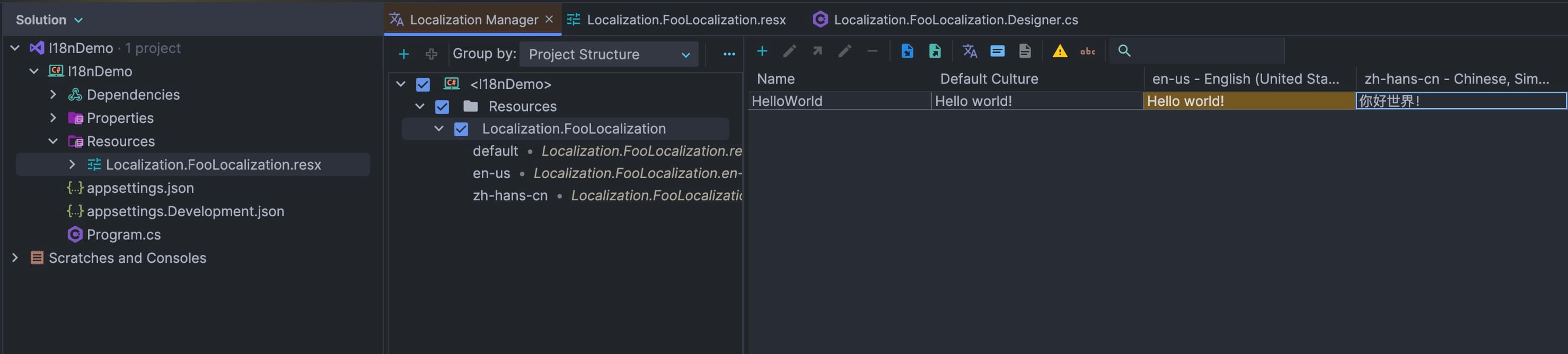
Add localization class
FooLocalization under the namespace Localization. Note that the class and namespace must comply with the resource file we created. 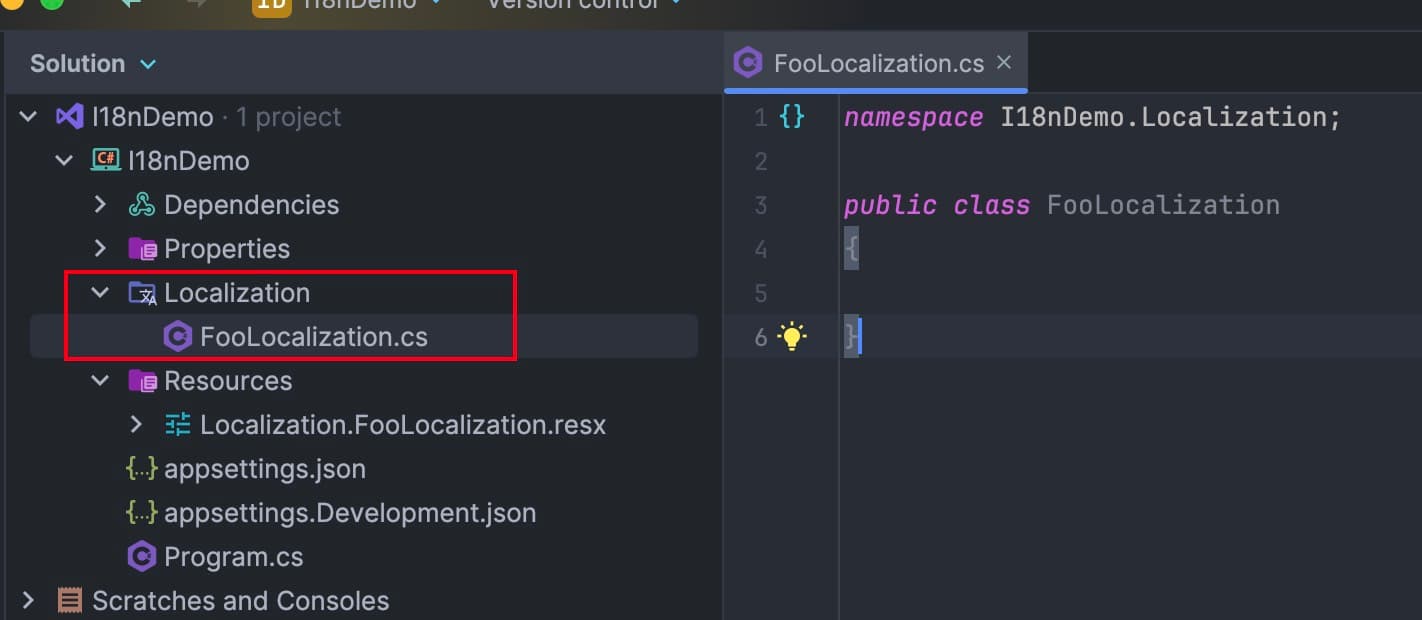
Just leave the class empty.
Configure resource path
builder.Services.AddLocalization(options =>
{
options.ResourcesPath = "Resources";
});
Use localization
Now you can inject IStringLocalizer<FooLocalization> to use the string:
app.MapGet("/",
([FromServices] IStringLocalizer<FooLocalization> fooLocalizer)
=> fooLocalizer["HelloWorld"].Value);
Enable translation
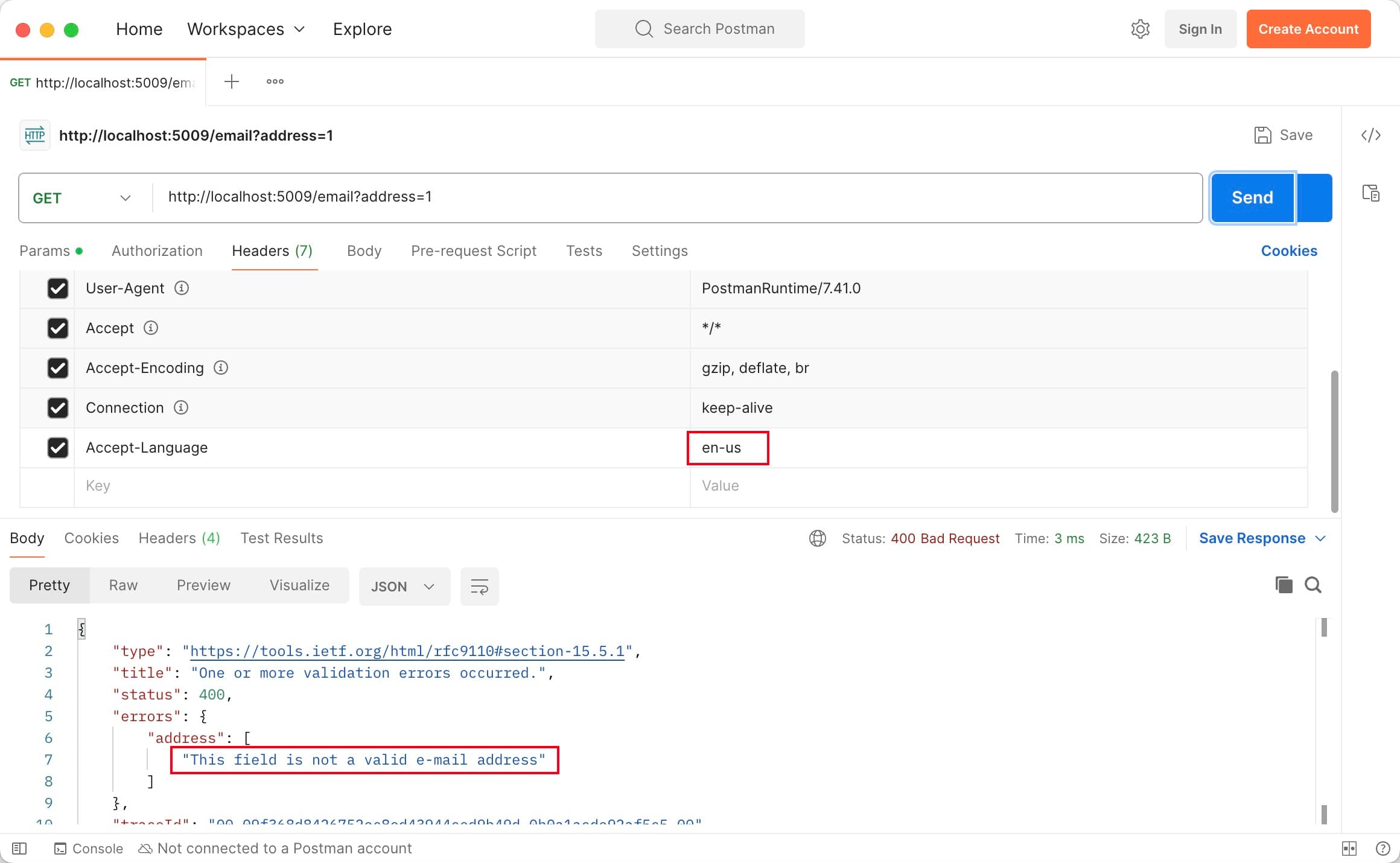
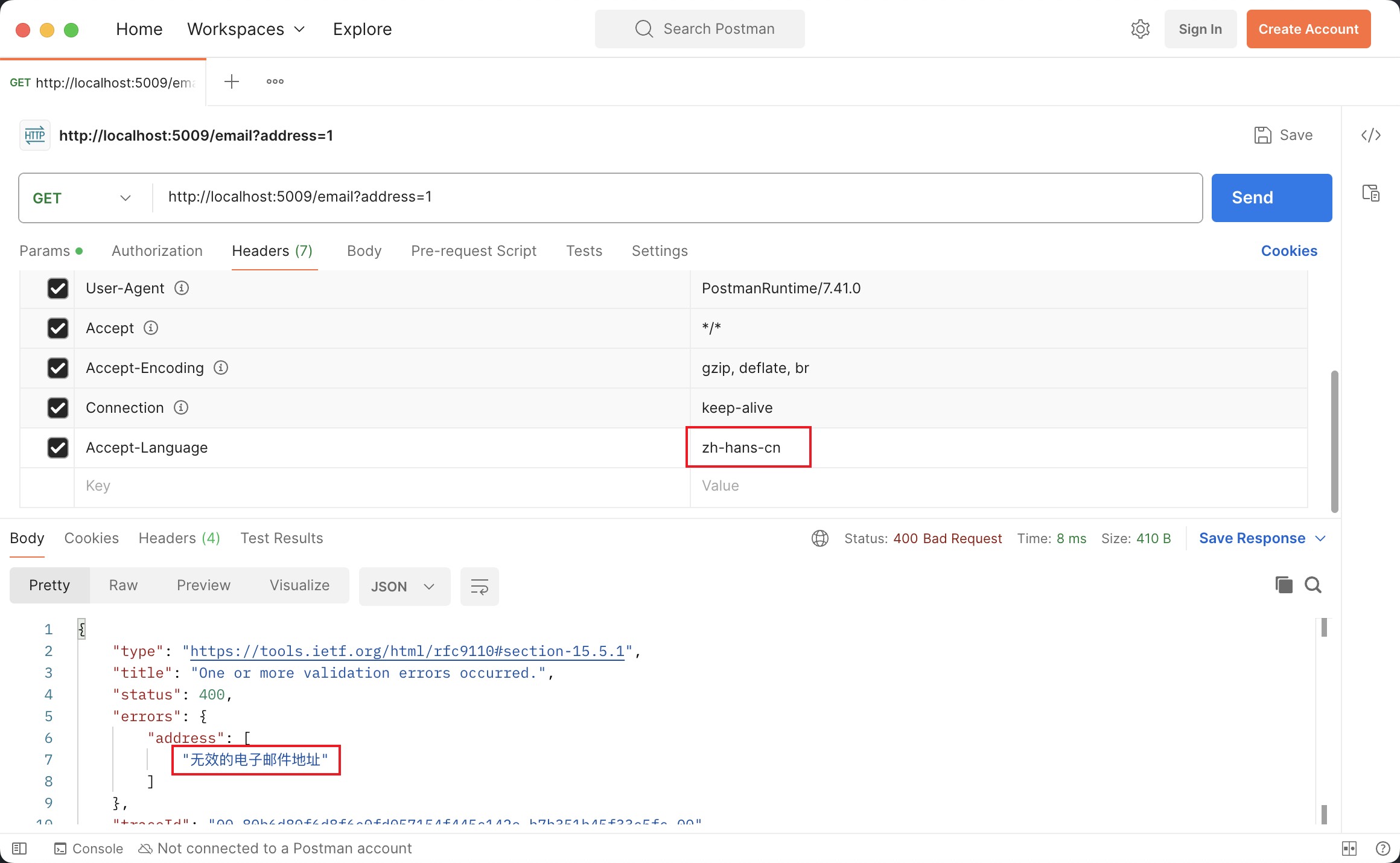
.NET provides an easy way to enable translation based on Accept-Language HTTP request header.
Firstly, you need to configure supported cultures:
builder.Services.Configure<RequestLocalizationOptions>(options =>
{
options.SetDefaultCulture("en-us")
.AddSupportedCultures(["en-us", "zh-hans-cn"])
.AddSupportedUICultures(["en-us", "zh-hans-cn"]);
});
Then, enable request translation:
app.UseRequestLocalization();
If you want route-based translation or a custom way to specify language, please refer to Implement a strategy to select the language/culture for each request in a localized ASP.NET Core app.
Now we have done. You can send requests to test it.
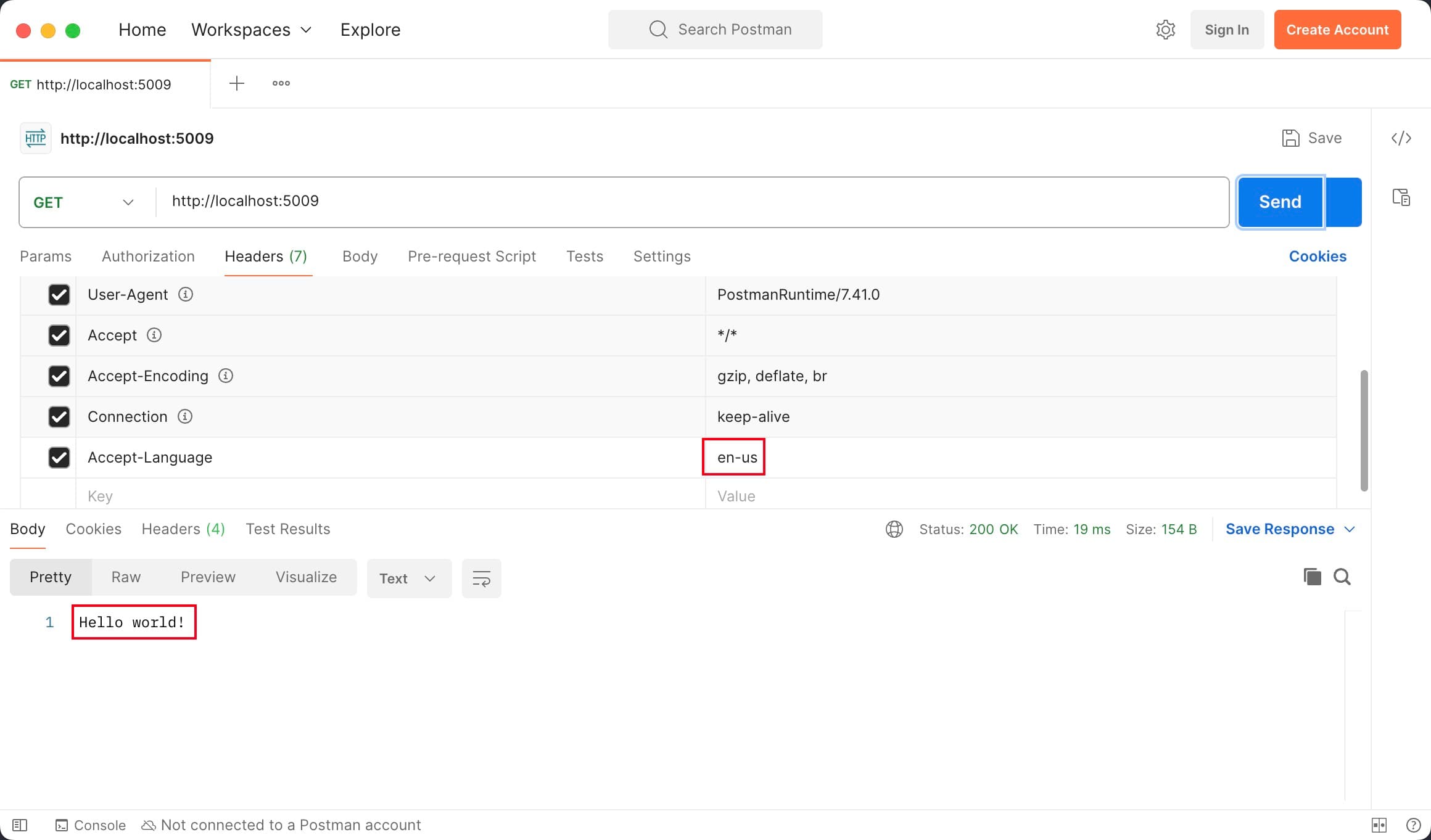
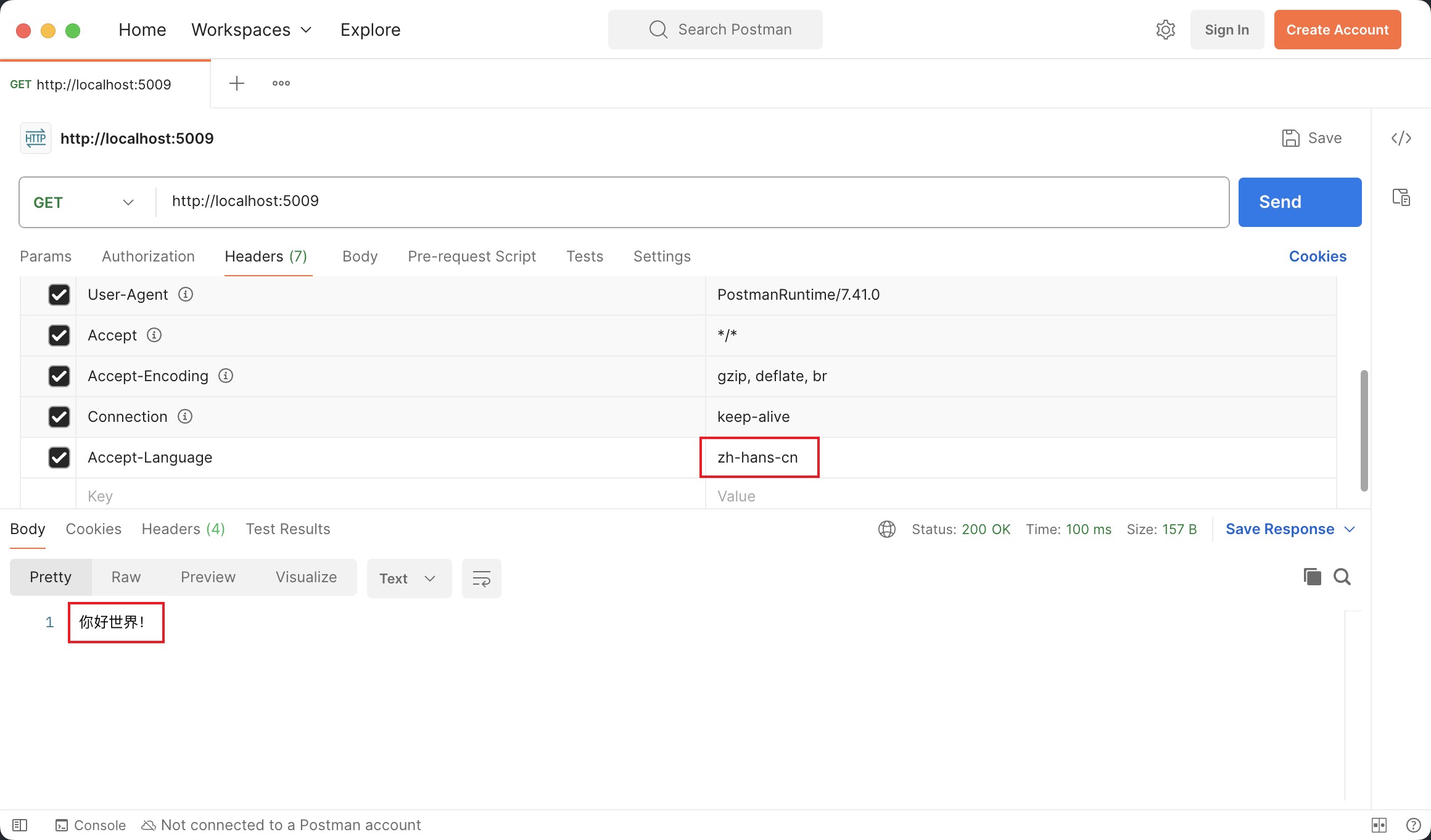
Enable data annotation localization
For data annotations, .NET indeed provides a solution for localization, unfortunately however, we have to translate the error messages by ourselves. Here is my preferred way.
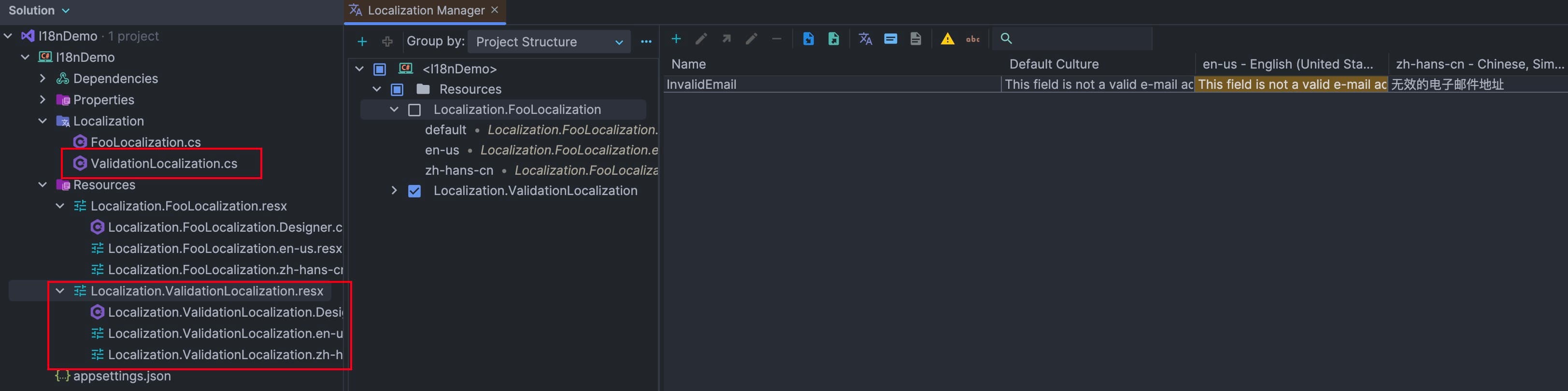
Then, configure to enable data annotation localization:
builder.Services.AddMvc()
.AddDataAnnotationsLocalization(options => {
options.DataAnnotationLocalizerProvider = (type, factory) =>
factory.Create(typeof(ValidationLocalization));
});
Finally, we specify error messages for data annotations. Note that this error message should be the name of the resource entry you have just created.
...But before that, remember currently data annotations only work for MVC, so we have to map MVC controllers.
app.MapControllers();
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace I18nDemo.Controllers;
[ApiController]
[Route("email")]
public class EmailController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Get([FromQuery] [EmailAddress(ErrorMessage = "InvalidEmail")] string address)
{
return Ok(address);
}
}
Reference
Official document: Globalization and localization in ASP.NET Core.